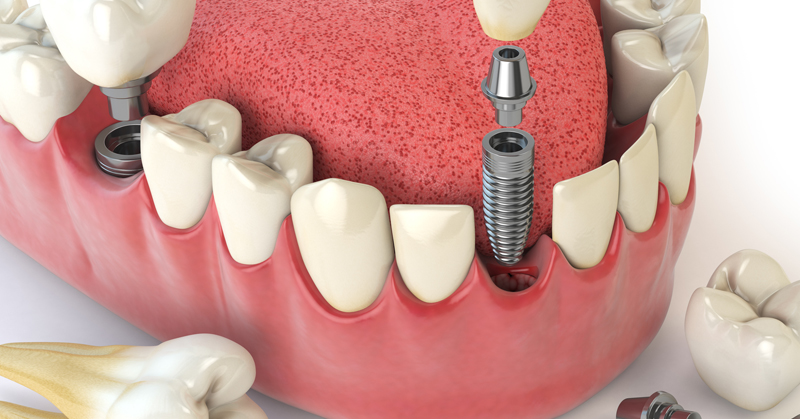
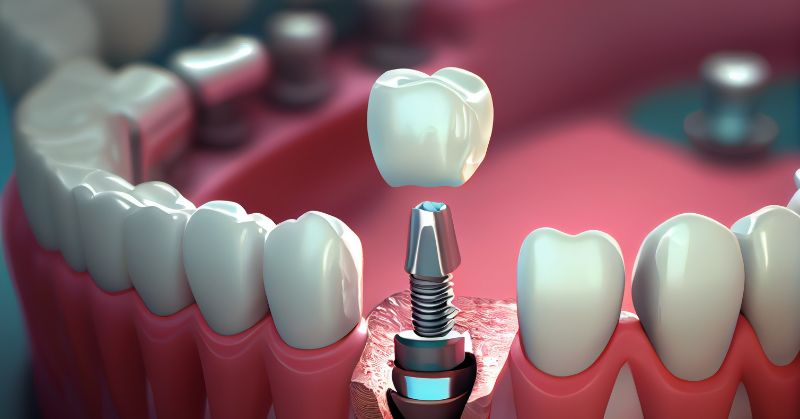
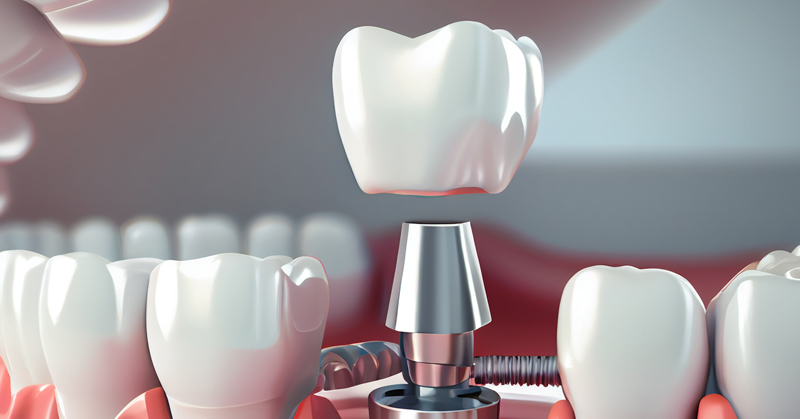
Do You Know All These Different Types of Implants?
In the field of dentistry, dental implants have revolutionized the way we approach tooth replacement. With their durability, functionality, and aesthetic appeal, dental implants have become the go-to solution for individuals with missing teeth. However, not all dental implants are created equal. There are various types of dental implants, each with its own unique characteristics and applications. In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the different types of dental implants and the techniques used for their placement.Why Are My Gum Swollen and Bleeding?
updated on November 15, 2023
It can be alarming when you notice your gums are swollen, red, and bleeding when you brush or floss. These symptoms should not be ignored, as they can signal the onset of gingivitis or more severe periodontitis. Gingivitis is inflammation of the gums caused by a buildup of plaque bacteria on teeth due to poor oral hygiene. As plaque increases, bacteria infect the gums, leading to swelling, tenderness, and bleeding. Without treatment, gingivitis can advance to periodontitis, where plaque spreads deeper below the gumline and causes worsening inflammation and potential tooth loss.
Gum swelling and bleeding is your mouth's way of signaling trouble. It most commonly occurs during puberty, pregnancy, stress, medication use, or chronic diseases like diabetes that reduce the body's ability to fight infection. Occasional spot bleeding may also arise from irritation or injury, such as overly forceful flossing. However, consistent swollen, tender, or bleeding gums should be evaluated by your dentist, as they likely indicate gingivitis. Proper oral hygiene and regular dental cleanings are key to treating and preventing further gum problems. Don't ignore irritated, bleeding gums - it is your mouth's call for help.
What causes gum swollen and bleeding?
Gennerally, mild or advanced gum disease are the primary causes of bleeding gums. But improper oral hygiene habits, use of certain medications, and some medical conditions can also irritate gums and make them more likely to bleed and swell. Practicing good oral hygiene and addressing any underlying factors are important for treating gum problems.
Gingivitis - The Most Common Cause
Gingivitis, a mild form of gum disease, is the leading cause of swollen, reddened gums that bleed during brushing and flossing. Gingivitis occurs when plaque, a sticky film containing bacteria, accumulates along and below the gumline due to inadequate oral hygiene habits. As plaque buildup persists, the plaque bacteria begin to infect the gums, triggering inflammation, tenderness, and easy bleeding. If left untreated, gingivitis can advance to periodontitis, a severe gum infection where plaque spreads deeper below the gumline, detaching gums from teeth and forming infected pockets that promote further bacteria proliferation and potential tooth loss.
Periodontitis - When Gingivitis Worsens
Periodontitis represents an advanced stage of gum disease that arises when gingivitis escalates due to poor oral hygiene. During periodontitis, plaque hardens into tartar that adheres firmly below the gumline. This causes gums to detach from teeth, forming infected pockets filled with plaque bacteria. Periodontitis leads to worsening gum inflammation, redness, swelling, bleeding, and potential tooth loss if treatment is not pursued.
Overbrushing - Aggressive Brushing Irritates Gums
Using a toothbrush that is too stiff or brushing aggressively with improper technique can damage gum tissues. This leads to sensitivity, swelling, and bleeding. Opting for a soft or extra-soft toothbrush and using gentle motions helps minimize gum irritation during brushing.
Medications - Blood Thinners Increase Bleeding Risk
Many medications like blood thinners, aspirin, and NSAIDs make patients more prone to bleeding gums by thinning the blood or interfering with clotting. Chemotherapy drugs and calcium channel blockers also increase gum bleeding risks. Consulting a dentist and making small oral hygiene adjustments can help combat side effects.
Underlying Conditions - Bleeding Disorders to Blood Cancers
Medical conditions that impair proper blood clotting or lower immunity can contribute to inflamed, bleeding gums. These include blood clotting disorders like hemophilia, chronic diseases like leukemia that affect platelet counts, autoimmune disorders, and vitamin C deficiency that slows wound healing. Managing the underlying condition is key to improving gum health.
How Do I Treat Gum Bleeding?
Treating swollen, bleeding gums starts with practicing good oral hygiene at home. Brush teeth gently twice per day with a soft-bristled toothbrush, using a gentle circular motion. Avoid scrubbing aggressively, which can damage gums further. Floss once daily to remove food particles and plaque from between teeth that brushing misses. Rinsing daily with warm salt water can also help reduce inflammation and cleanse the mouth.
Seeing a dentist for professional cleanings and treatment is key if swelling and bleeding persist despite home care. For mild gingivitis, the dentist will perform a thorough cleaning to remove plaque buildup and tartar below the gumline. Further options include gum scaling and root planing to reduce periodontal pockets, antimicrobial rinses to fight infection, and laser gum therapy to stimulate gum healing.
For more severe periodontal disease, antibiotics may be prescribed to combat infection alongside deep cleanings. If swelling is isolated around a particular tooth, it may signal an abscess requiring a root canal or tooth extraction. Surgery may be warranted in advanced cases to cut away infected gum tissue or regenerate bone loss using grafting.
If there is no clear gum disease, the dentist may refer you to a physician to diagnose potential causes like vitamin deficiencies, autoimmune disorders, diabetes, or blood cancers like leukemia that reduce the body's ability to control inflammation and bleeding. Your doctor can order lab tests and imaging scans to pinpoint the issue.
Home remedies like ice packs, over-the-counter pain relievers, warm compresses, and antioxidant-rich foods can temporarily alleviate discomfort from irritated gums. But it's critical to continue brushing twice daily even if mild bleeding occurs initially. See a dentist promptly if swelling lasts longer than 1-2 weeks or bleeding becomes severe despite home care. Treating gum issues early is key to preventing significant damage long-term. With a combination of proper daily oral hygiene and professional dental care, swollen, bleeding gums can be cured.

free&low-cost dental clinics
View Now
dental health

Dental Implants

Dental Implants
Why Are Implants So Expensive?
According to recent statistics, tooth loss is a prevalent issue, especially among older individuals. Adults between the ages of 20 to 64 have an average of 25.5 remaining teeth. However, factors such as age, smoking, lower income, and education level can contribute to a higher likelihood of tooth loss. In this article, we will explore dental implants in detail through the following aspects:
Dental Implants
How Can I Get Government Grants for Dental Implants?
Dental implants are a sought-after solution for missing teeth, offering a long-term fix that can significantly improve quality of life. However, the cost of dental implants can be prohibitive for many. Understanding government programs and other grants available for dental care, particularly dental implants, can help bridge this financial gap. In this guide, we will walk you through some government assistance and grant programs aimed at making dental implants more accessible.
Dental Implants
How Painful is Dental Implant Surgery?
If you are missing teeth due to decay, injury, or gum disease, dental implants offer an effective and natural-looking replacement option. Unlike removable dentures that can slip, implants fuse securely into your jawbone for permanent stability. They also help preserve bone and support surrounding teeth better than bridges or dentures. But most patients wonder - how painful are implants? The procedure does involve surgery and recovery time.
Dental Implants
Top Dental Implant Brands in the United States
When it comes to dental implants, finding a reputable and reliable dental implant service is crucial. Dental implants are a popular and effective solution for replacing missing teeth, providing individuals with improved aesthetics, functionality, and oral health.With the increase in demand for dental implants, numerous brands have emerged, providing a variety of options to meet the diverse needs and budgets of patients. Choosing the right dental implant brand is vital as it directly affects the success and longevity of the dental implant procedure. In this article, we will explore some of the top dental implant brands in the United States, known for their expertise, advanced technology, and exceptional patient care.
Dental Implants
Will Your Insurance Cover Dental Implants?
Dental implants are growing in popularity, with over 3 million Americans choosing them to replace missing teeth. While implants fuse securely into the jawbone providing natural-looking and long-lasting tooth replacements, the process does come with a hefty price tag. On average, a single implant can cost $1,600-$2,200 out of pocket. For patients needing multiple implants or other restorative work, these expenses quickly add up.